The stock market, a dynamic and complex environment, can be intimidating for beginners. However, with the right knowledge and approach, investing in stocks can be a rewarding way to build wealth over time. In this guide, the fundamentals of stock market investing for beginners will be explored, utilizing passive voice for clarity and simplicity.
Understanding the Stock Market
The stock market is comprised of exchanges where shares of publicly traded companies are bought and sold. Stocks, also known as shares or equities, represent ownership in a company. When stocks are purchased, an investor essentially buys a small piece of that company.
The Importance of Research
Before investments are made, thorough research must be conducted. The financial health, business model, and growth potential of companies should be analyzed. Information can be gathered from company financial statements, news reports, and stock analysis websites. Understanding market trends and economic indicators can also provide valuable insights.
Setting Investment Goals
Investment goals should be clearly defined. Investors must determine whether the aim is short-term gains or long-term wealth accumulation. Risk tolerance should also be assessed, as stock investments can be volatile. A diversified portfolio, containing a mix of stocks from different sectors, is often recommended to spread risk.
Opening a Brokerage Account
A brokerage account must be opened to start investing in stocks. Various online brokers offer different features, fees, and tools. The selection of a brokerage should be based on individual needs and preferences. Once the account is funded, stocks can be purchased through the broker’s trading platform.
Choosing Stocks
Stocks should be selected based on research and investment goals. Companies with strong financial performance and growth potential are often preferred. Stocks can be categorized into different types, such as blue-chip stocks, growth stocks, and dividend stocks. Blue-chip stocks are from well-established companies with a history of stability. Growth stocks belong to companies expected to grow at an above-average rate, while dividend stocks provide regular income through dividend payments.
Understanding Stock Prices
Stock prices fluctuate based on supply and demand. When more investors want to buy a stock than sell it, the price goes up. Conversely, when more investors want to sell a stock than buy it, the price goes down. Factors such as company performance, industry trends, and economic conditions influence these price movements.
Investing Strategies
Various strategies can be employed in stock market investing. Some popular strategies include:
- Buy and Hold: Stocks are purchased and held for an extended period, regardless of market fluctuations. This strategy relies on the long-term growth potential of the stock market.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: A fixed amount of money is invested at regular intervals, regardless of the stock price. This approach reduces the impact of market volatility.
- Value Investing: Stocks are selected that appear undervalued based on fundamental analysis. This strategy focuses on buying stocks at a lower price than their intrinsic value.
- Growth Investing: Investments are made in companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to other companies. These stocks often do not pay dividends, as profits are reinvested to fuel growth.
Risks and Rewards
Investing in the stock market carries risks, including the potential loss of capital. Market volatility, economic downturns, and poor company performance can negatively impact stock prices. However, the potential for high returns makes stock market investing appealing. Historically, stocks have provided higher returns compared to other investment types, such as bonds or savings accounts.
Monitoring Investments
Once stocks are purchased, investments should be regularly monitored. Company performance, market conditions, and economic indicators should be reviewed. Adjustments to the portfolio may be necessary based on changes in investment goals or market conditions. It is important to remain patient and avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations.
Tax Considerations
Taxes on stock market investments should not be overlooked. Capital gains tax is applied to profits made from selling stocks at a higher price than the purchase price. The rate of capital gains tax can vary depending on the holding period and individual tax bracket. Dividends received from stocks are also subject to taxation. Consulting a tax professional is advisable to understand the specific tax implications of stock market investments.
How to make money with low risk
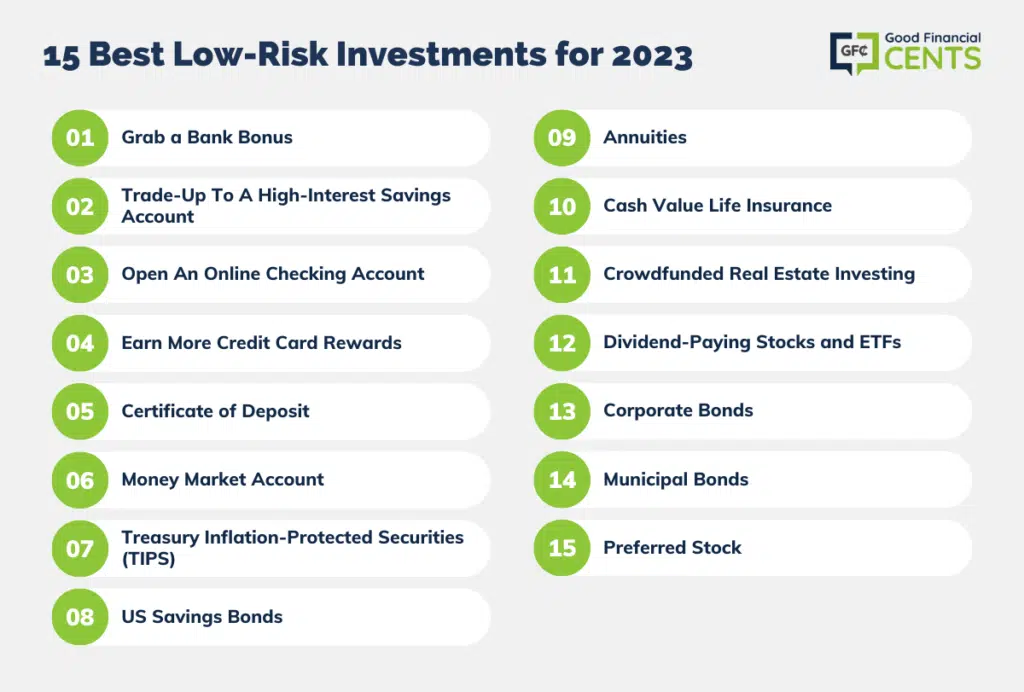
Investing in the stock market has long been considered a pathway to financial growth and wealth accumulation. For those seeking to make money with low risk, a strategic approach must be taken. The principles of diversification, long-term investing, and the utilization of index funds and bonds can help achieve this goal. This log will explore various strategies and considerations for low-risk stock market investing.
Understanding Low-Risk Investments
Low-risk investments in the stock market aim to provide steady, reliable returns while minimizing the potential for significant losses. The main objective is to preserve capital and ensure a consistent, albeit modest, growth over time.
Diversification: The Key to Minimizing Risk
Diversification plays a critical role in risk management. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions, the impact of any single asset’s poor performance is reduced. This strategy ensures that even if some investments underperform, others may perform well, balancing the overall portfolio.
Index Funds: A Safe Bet
Index funds are highly recommended for low-risk investing. These funds replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. By investing in an index fund, exposure to a broad market is gained, which inherently diversifies the investment. Index funds typically have lower fees compared to actively managed funds, which further enhances returns over time.
Bonds: Stability and Income
Bonds are another crucial component of a low-risk investment strategy. They provide stability and a steady income stream through interest payments. Government bonds, particularly U.S. Treasury bonds, are considered among the safest investments, as they are backed by the government’s full faith and credit. Corporate bonds, while slightly riskier, can offer higher returns and still contribute to the portfolio’s overall stability.
Dividend-Paying Stocks: Regular Income
Investing in dividend-paying stocks can provide a regular income stream. These companies distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. High-quality, established companies with a history of consistent dividend payments are preferable, as they are generally more stable and less volatile.
Long-Term Investment Horizon
Adopting a long-term investment horizon is crucial for minimizing risk in the stock market. Short-term market fluctuations can be unpredictable and volatile, but over the long term, the stock market has historically trended upward. By holding investments for an extended period, the effects of short-term volatility are mitigated, and the potential for higher returns increases.
Dollar-Cost Averaging: Reducing Market Timing Risk
Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the market’s performance. This approach reduces the risk associated with trying to time the market and ensures that investments are made consistently. Over time, this strategy can lower the average cost per share, as purchases are made both when prices are high and when they are low.
Rebalancing: Maintaining the Desired Risk Level
Regular portfolio rebalancing is essential to maintain the desired level of risk. As certain investments outperform others, the portfolio’s asset allocation may drift from its original target. By periodically rebalancing, the portfolio is realigned with the investor’s risk tolerance and investment goals. This process involves selling a portion of the overperforming assets and reinvesting in underperforming ones.
Understanding Market Conditions
Staying informed about market conditions and economic indicators is important for low-risk investing. Awareness of interest rates, inflation, and overall economic health can help make informed decisions about asset allocation and timing. While low-risk investors should not be swayed by short-term market movements, understanding the broader economic context can provide valuable insights.
Utilizing Professional Advice
Seeking professional financial advice can further enhance a low-risk investment strategy. Financial advisors can provide personalized guidance based on individual risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment horizon. They can also help navigate complex investment products and ensure that the portfolio is well-diversified and aligned with the investor’s objectives.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
To succeed in low-risk stock market investing, certain common pitfalls must be avoided. Emotional decision-making, chasing high returns, and failing to diversify are some of the mistakes that can increase risk. Sticking to a well-thought-out investment plan and maintaining discipline is crucial for long-term success.
Conclusion
Stock market investing, when approached with the right knowledge and strategy, can be a powerful tool for wealth building. Beginners are encouraged to start with thorough research, clear investment goals, and a diversified portfolio. While risks are inherent in stock market investing, the potential rewards can be substantial. Patience, discipline, and continuous learning are key to successful investing.
By following these guidelines, a solid foundation for stock market investing can be established, paving the way for financial growth and security.










