Impact of Government Policies on Economic Growth
Government policies have long been recognized as pivotal determinants of economic growth. Through various legislative and regulatory measures, governments influence the economic environment, shaping the trajectory of national economies. The impact of these policies on economic growth can be observed in several key areas: fiscal policy, monetary policy, trade policy, and regulatory frameworks.
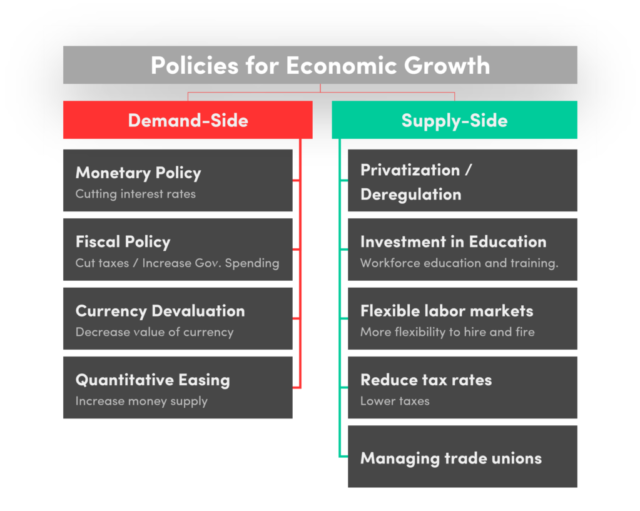
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy, encompassing government spending and taxation, is one of the primary tools utilized to stimulate or restrain economic activity. Public investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare have been shown to significantly enhance productivity and long-term economic growth. For instance, infrastructure projects, such as the construction of roads, bridges, and public transport systems, facilitate commerce by reducing transportation costs and increasing connectivity. Investments in education and healthcare improve the quality of the labor force, thus boosting productivity and innovation.
Conversely, fiscal austerity measures, often implemented to reduce budget deficits, can hinder economic growth in the short term. Cuts in public spending typically lead to reduced aggregate demand, potentially resulting in higher unemployment rates and slower economic recovery. Tax policies also play a crucial role. Progressive taxation, where higher income earners are taxed at higher rates, is often used to redistribute income and reduce inequality. However, excessively high tax rates can discourage investment and entrepreneurial activities, negatively impacting economic growth.
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy, managed by central banks, involves the regulation of the money supply and interest rates to control inflation and stabilize the economy. Lowering interest rates makes borrowing cheaper, encouraging investment and consumer spending, which in turn stimulates economic growth. Conversely, raising interest rates can help control inflation but may also slow down economic activity by making loans more expensive and reducing consumer spending.
Quantitative easing, a non-traditional monetary policy tool, involves the purchase of government securities or other securities from the market by the central bank to increase the money supply and encourage lending and investment. This policy has been used extensively in the wake of economic crises to support financial markets and spur economic growth. However, prolonged periods of low-interest rates and extensive quantitative easing can lead to asset bubbles and financial instability, which may pose risks to long-term economic growth.
Trade Policy
Trade policies, including tariffs, trade agreements, and import/export regulations, significantly influence economic growth. Free trade agreements, by reducing or eliminating tariffs and other trade barriers, promote increased trade between countries. This can lead to a more efficient allocation of resources, greater competition, and access to a wider variety of goods and services, all of which contribute to economic growth.
Protectionist policies, on the other hand, aim to shield domestic industries from foreign competition through tariffs and import restrictions. While these policies can protect jobs and industries in the short term, they often lead to higher prices for consumers and inefficiencies in the economy. Over time, protectionism can stifle innovation and reduce the competitiveness of domestic industries, ultimately hindering economic growth.
Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory policies, encompassing labor laws, environmental regulations, and business regulations, also have significant implications for economic growth. Well-designed regulations can promote fair competition, protect consumers, and ensure sustainable development. For example, labor laws that ensure fair wages and working conditions can contribute to a more motivated and productive workforce, while environmental regulations can promote sustainable economic practices.
However, overly stringent regulations can impose significant costs on businesses, reducing their ability to invest and expand. Excessive bureaucratic red tape can stifle entrepreneurship and innovation, deterring investment and slowing economic growth. Therefore, finding the right balance in regulatory frameworks is crucial for fostering an environment conducive to economic growth.
Case Studies
Several case studies illustrate the profound impact of government policies on economic growth. The post-World War II economic boom in the United States was driven by a combination of expansive fiscal policies, including the GI Bill and massive infrastructure investments, and accommodative monetary policies. Similarly, the rapid economic growth in China over the past few decades can be attributed to significant economic reforms, including the liberalization of trade policies and the introduction of market-oriented reforms.
In contrast, the economic stagnation experienced by Japan in the 1990s, known as the “Lost Decade,” has often been attributed to a combination of restrictive fiscal policies, ineffective monetary policies, and structural issues within the economy. The austerity measures implemented by several European countries in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis also provide a stark example of how government policies can impact economic growth. While these measures aimed to reduce budget deficits, they often led to prolonged periods of economic stagnation and high unemployment rates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, government policies play a crucial role in shaping economic growth. Through fiscal, monetary, trade, and regulatory policies, governments can influence the economic environment and steer the economy towards growth or contraction. While well-designed policies can promote economic stability and long-term growth, poorly conceived or overly restrictive policies can hinder economic progress and exacerbate economic challenges. Therefore, policymakers must carefully consider the implications of their decisions and strive to create a balanced and conducive environment for sustainable economic growth.